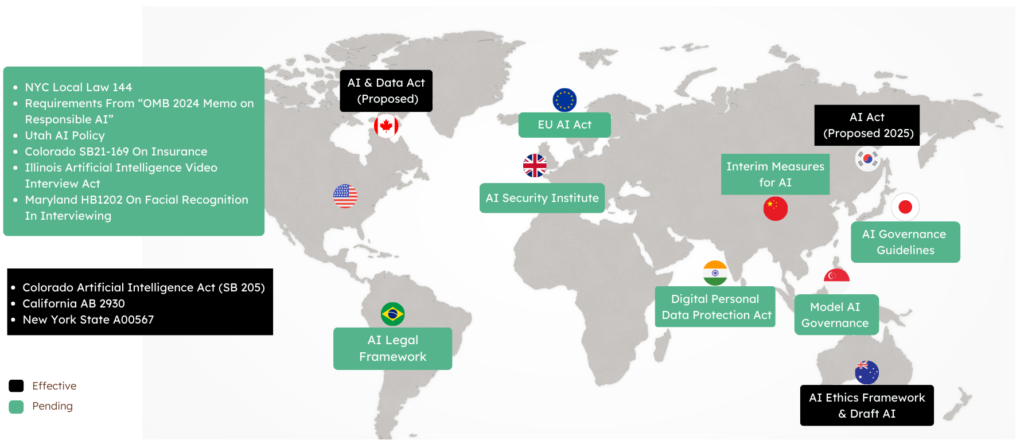
A Rise in AI Regulation Globally
Strategic Recommendations for 2025




Audit AI Systems:
Periodically review the implementation of new requirements especially on high-risk and self-generative AI systems.
Strengthen Governance:
Establishing a robust AI governance frameworks including clear accountability and human oversight.
Enhance AI Literacy:
Implement training programs for employees to comply with mandatory literacy standards, for example in the EU.
Monitor Global Trends:
Keep up to date with regional information, particularly in fast-moving regions such as Asia-Pacific and Africa.
In 2025, it will be a turning point for the legislation of Artificial Intelligence towards rigorous regulatory framework that will lead to influence on global adoption of the technology.
Significance in Today's Landscape
As AI becomes more pervasive, global regulatory strides are increasing. For example, the United States, Singapore, China and the European Union are all taking steps to establish context specific regulatory mechanisms. Each region is looking to address individual AI regulatory concerns around data privacy, ethical AI frameworks and accountability against the backdrop of regional societal norms and economic priorities including:
- European Union: The EU is moving forward with the AI Act regulation framework which attempts to regulate AI systems according to their risk levels. This far-reaching regulation could become one of the world’s toughest AI laws by guaranteeing consumer protection, transparency and accountability.
- United States: The US is promoting a sectoral regulatory approach with a number of proposals around privacy protection and fair competition, announcing – most recently in executive orders and legislative proposals – safety in AI, bias mitigation, and the retention of tech leadership.
- China: Chinese regulation focuses on national security and social stability with an AI governance and control policy designed to avoid abuse. China has proposed broad restrictions on generative AI, particularly around content development and social media, stressing the need to match AI development to government policies.
- Singapore: Widely acclaimed for its forward-looking digital policy framework, Singapore is moving toward “ethical by design,” encouraging companies to adopt principles of transparency and accountability in its Model AI Governance Framework, thus balancing the promotion of innovative AI while protecting ethical AI use.
Main AI Regulation by Jurisdiction
| Country/Region | AI Plans and Developments | Key Highlights | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| European Union | Preparing for the EU AI Act, focusing on prohibitions (Article 5) and mandatory AI literacy (Article 4). |
|
EU AI Act |
| Australia | Published AI and ESG guidance emphasizing responsible AI’s role in advancing ESG goals. |
|
Australian Government and Office of the Australian Information Commissioner Guidance |
| United States | The Department of Labor issued workplace AI guidelines focusing on transparency and ethical use. |
|
US Department of Labor Guidelines (October 2024), White House National Security Memo |
| Poland | Opened consultations to align national legislation with the EU AI Act. |
|
Polish Ministry of Digital Affairs Announcement, October 2024 |
| Hong Kong | Released a dual-track AI policy for financial markets. |
|
Hong Kong Government Policy Statement, October 2024 |
| Japan | Issued AI safety and red teaming guidance with a focus on human-centric principles. |
|
Japanese AI Safety Institute Guidance and Japan Fair Trade Commission Consultation |
| United Kingdom | Launched the Regulatory Innovation Office (RIO) to support tech innovation. |
|
UK Department for Science, Innovation, and Technology Announcement, October 2024 |
| G7 Nations | Held a summit to address competition concerns related to AI development. |
|
G7 Competition Summit Statement, October 2024 |
WHO DOES IT IMPACT?
Any firm that relies on AI models in their decision making
Asset Managers
Banks
Supervisors
Commodity Houses
Fintechs
How Can We Help?
Working with senior AI and Compliance advisors who are at the forefront of AI supervisory dialogue, we can support the below activities
The following steps can summarise it:
1
Training & Culture change
- Design training programs for organization-wide needs
- Deliver C-suite/senior manager/company introduction to AI and in-depth AI risk management trainings
- Deliver AI literacy EU AI Act expectations training
- Write / co-design AI Principles and policies
- Design processes for internal and/or external stakeholder consultation
2
Maturity Assessments
- Create fairness and impact testing frameworks that can be integrated into the AI development pipeline.
- Map and report existing responsible AI and AI governance efforts against proprietary FIPA maturity curve. Identify next steps to mature along the FIPA curve
- Advise on 3P considerations and decision-planning
- Mitigation Plans: Develop tailored mitigation strategies for each risk, prioritizing high-risk applications.
- Conduct audit/assessment/conformity assessment (TBD. Requires more research)
- Model validation
3
Governance Optimisation
- Set up AI review boards, escalation paths, incident response plans, and decision-making processes
- Design documentation requirements for high-risk AI systems
- Template transparency reports for C-suite/Boards/publication
4
Risk Management
- Design AI risk management framework (from scratch)
- Adapt existing risk management frameworks to account for AI
- Build evaluation frameworks for identifying and prioritizing AI impact
- Design and conduct scenario planning and horizon scanning exercises to get ahead of emerging AI risks <likely expand existing operational resilience efforts>
5
Specialized expertise : Large & Advanced Companies
- Review and provide guidance on Transparency Report
- Conduct exercises to clarify tradeoffs for improved decision-making (e.g. privacy v fairness v accuracy v transparency v opportunity costs)
- Validate/challenge existing AI governance and Responsible AI efforts
- Conduct assessment against proprietary FIPA maturity curve. Produce a report for management on gaps and requirements to advance maturity and achieve best-in-class AI governance
- Design risk management processes and structures for emerging, unproven and early stage technologies
- Inform risk-based scaled versus bespoke risk management protocols
6
Establish a Global AI Compliance Framework
- Centralized Governance: Create a centralized governance structure to oversee AI compliance globally, led by a Chief AI Officer or Compliance Lead.
- Local Adaptation: Appoint regional compliance officers to adapt the global framework to local regulatory requirements (e.g., EU AI Act, US NIST Framework, Australian Privacy Act).
- Algorithmic Accountability: Document AI system design, data sources, and decision-making processes to demonstrate compliance.
- Uniform Standards: Implement baseline AI ethical and governance principles (aligned with global standards such as OECD AI Principles and ISO standards) to ensure consistency across jurisdictions.
Want to hire
AI Regulation Expert?
Book a call with our experts