Independent Review of Risk Management Framework
Risk FrameworkFramework
A risk management framework is a structured methodology organizations employ to identify, assess, manage, and monitor risks. It provides a systematic means to make decisions and allocate resources by understanding uncertainties that could influence an organization’s objectives, especially to a financial institution (FRFI).
A good RMF is not static—it is continuously recalibrated, audited, and aligned to internal and external change. It bridges operational, financial, reputational, and ethical risk dimensions, enabling the bank to not just withstand shocks—but shape the market response to them.
DOWNLOAD RISK FRAMEWORK GUIDELINE
Get your free copy of Independent Risk Framework Guideline
Overview of Topic
Whether it is related to the set up on a new business or an independent review of the Risk Management Framework (RMF) it is crucial to ensuring sound capital management and provide assurance to key stakeholders (shareholders, Board, customers and others).
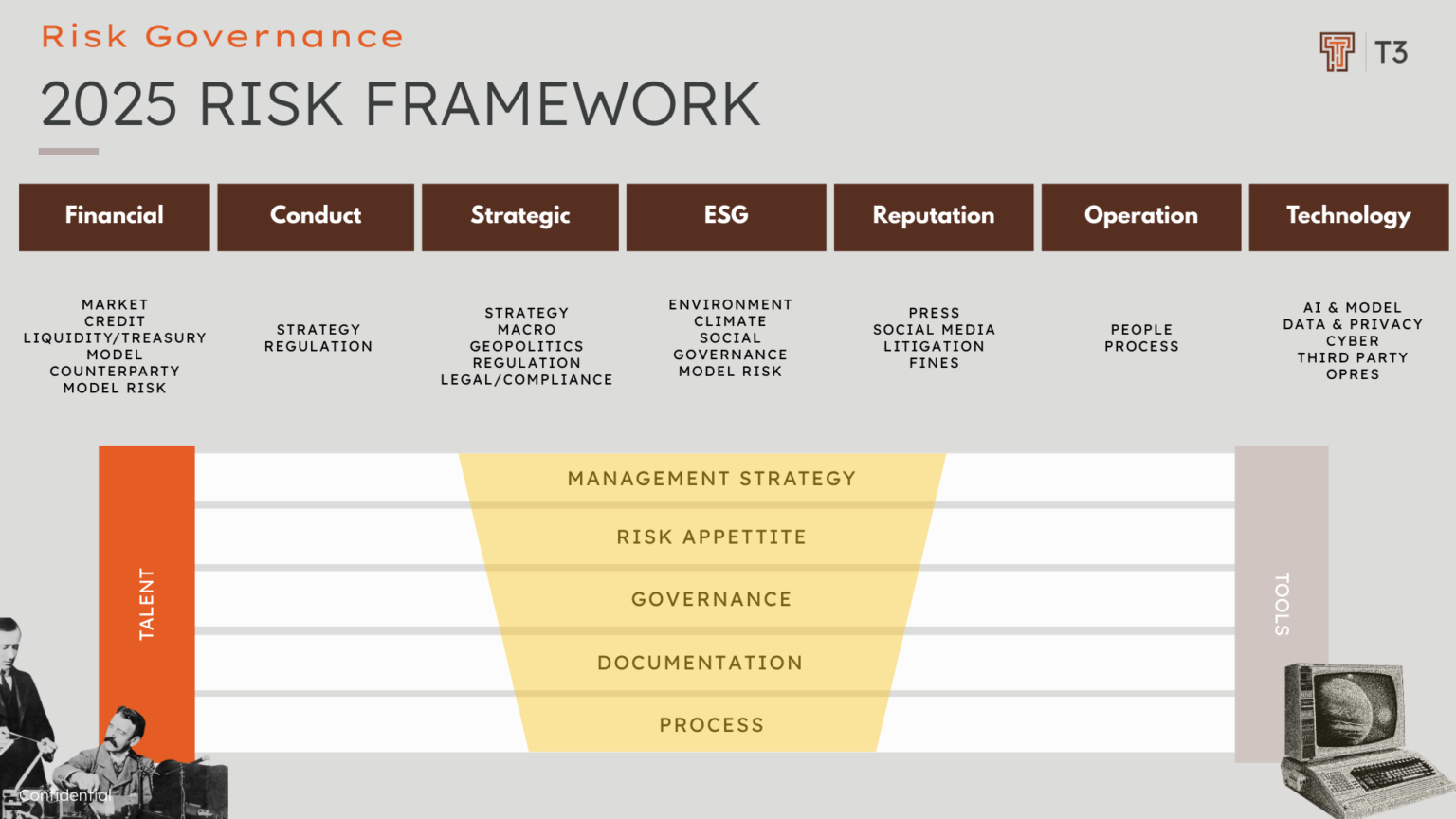
Key components of a risk framework typically include:
1. Risk Identification:
- Identifying potential, existing and future operational risks to the organization, which may exist in various forms (financial, operational, strategic, legal, or reputational)
- Risk Taxonomy: Customised, multi-dimensional, and updated quarterly with regulatory radar overlays (e.g., FCA/PRA thematic priorities, ESMA Risk Dashboard).
- Horizon Scanning: Systematically integrated via internal audit, strategy, compliance, and external advisory partnerships (e.g., legal, geopolitical, cyber threat intel).
Innovation: Incorporates a “Black Swan Readiness Index”—scoring scenarios for surprise potential and preparedness gaps.
2. Risk Assessment and Analysis:
Analysis of the potential impact and likelihood of identified risks to allow prioritisation of action or resource need.
- ICARA / ICAAP Alignment: Risk exposures feed into both Pillar 2A and Pillar 2B. All material risks must demonstrate capital or non-capital mitigants.
- Stress Testing Architecture: Bottom-up and top-down dual engine with reverse stress testing linked to strategic failure modes (e.g., cyber-triggered mass redemption).
- Liquidity Risk: Real-time cash-flow modelling with predictive analytics linked to behavioural runoff profiles (PSD2-style data on account usage).
3. Risk Mitigation Strategies including Risk Appetite:
Developing strategies to treat identified risks, from avoidance, transference, sharing or acceptance of the risk, depending on the nature and severity of it. The risk appetite of the business is relevant.
- Philosophy: Risk is not simply a constraint; it is a strategic variable. The RMF enables informed risk-taking in pursuit of sustainable growth, resilience, and purpose.
- Risk Appetite: Quantified and qualitative boundaries are board-owned and tiered across financial, non-financial, and emerging risk domains. It is dynamic—linked to scenario-adjusted capital projections and strategic planning cycles.
- Culture: Codified through a “Three Lines of Accountability” (not just defence) model, with incentive structures explicitly tied to risk outcomes (per PRA and EBA expectations).
4. Implementation of Controls:
The application of appropriate controls and measures to manage or mitigate specific risks. These could be preventative and detective controls, which could be in the form of policies, procedures, or technological solution. A robust framework can also support this.
5. Monitoring and Reporting:
Continuing monitoring of risk processes and controls to determine effectiveness. Risks and their management should be reported to the relevant key stakeholder (including to senior management and, in certain conditions, to external stakeholders). A return footnote can be required in some cases.
6.Review and Adaptation:
The risk framework is not static and requires periodic review so it can respond to current risks or changes to an organization’s external and internal environment.
This structured approach allows organizations to make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and enhance their resilience against potential adverse events.
Significance in Today's Landscape
Recent corporate failures highlight the grave consequences of inadequate risk management. The collapses of major banks in 2023 were linked to ambitious business strategies and weak risk management processes, exacerbated by aggressive growth reliant on less durable funding. Senior management actions at these banks further underscore governance defects, as substantial stock sales immediately before the collapse of one bank, suggest poor risk management and governance practices might have been involved.
In absence of a robust risk management framework, companies face acute exposure to complex risks that can rapidly escalate into an existential threat, putting at stake stakeholders’ and the wider financial ecosystem’s interests, to include compliance risk and regulatory compliance risk. Recent corporate failures highlight the grave consequences of inadequate risk management. The collapses of major banks in 2023 were linked to ambitious business strategies and weak risk management processes, exacerbated by aggressive growth reliant on less durable funding. Executive leadership actions at these banks further underscore governance defects, as substantial stock sales immediately before one bank’s collapse suggest poor risk management and governance practices in play.
WHO DOES IT IMPACT?
Asset Managers
Banks
Commodity House
Fintechs
How Can We Help?
1
Policy Review
Our risk management experts assess the adequacy and effectiveness of risk management policies in place, ensuring policies are in line with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
2
Procedure Assessment
Our senior risk consultants evaluate the efficacy and efficiency of risk management procedures, identifying areas for improvement to ensure robust risk identification, assessment, and mitigation.
3
Data Quality Inspection
Our technical risk managers assess the accuracy, completeness, and timeliness of risk data, ensuring data integrity for informed decision-making and accurate risk reporting
4
Reporting Evaluation
Our risk SMEs assess the effectiveness of risk reporting mechanisms, ensuring timely and accurate communication of risk positions to stakeholders
5
Measure Examination
Our quantitative risk quants can evaluate the appropriateness of risk measures employed, identifying any gaps or inconsistencies in risk measurement and suggesting improvements.
6
Governance Review
Our senior risk specialists will assess the structure and effectiveness of risk governance frameworks. This will ensure clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability in managing risks.
7
Implementation Assessment
Senior risk professional evaluating the execution of risk management strategies and plans to identify any areas of non-compliance or inefficiency and recommending corrective actions.
8
Benchmarking Against Best Practices and Regulation
Our most senior risk experts assess the existing risk management framework against industry best practices, regulatory requirements, and strategic objectives, providing recommendations for alignment and enhancement to achieve a mature and resilient risk management framework.
Frequently Asked Questions
The five key components of a risk framework (or risk management framework) are:
- Risk Identification: Detecting internal and external risks that could impact business objectives.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks.
- Risk Mitigation: Designing controls and strategies to manage or reduce risk.
- Monitoring and Review: Continuously tracking risk exposure and the effectiveness of controls.
- Governance and Reporting: Ensuring accountability and clear communication of risk across the organization.
At T3, we tailor these components to align with your regulatory environment and strategic goals.
A comprehensive risk management framework (RMF) often includes these seven elements:
- Risk Context Definition: Establishing scope, objectives, and appetite.
- Risk Identification: Mapping potential threats and opportunities.
- Risk Analysis: Assessing risk level using quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Risk Evaluation: Comparing risk levels to thresholds and appetite.
- Risk Treatment: Implementing mitigation plans or accepting risk.
- Communication and Consultation: Ensuring stakeholders are engaged and informed.
- Monitoring and Review: Continuously improving the framework based on performance and emerging risks.
These elements reflect best practices from ISO 31000 and regulatory guidance. T3 helps you embed these principles into your business-as-usual activities for long-term resilience.
A risk management framework typically includes:
- Risk Policy and Appetite Statement
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Risk Assessment Methodology
- Control Framework
- Escalation and Reporting Protocols
- Ongoing Monitoring Mechanisms
- Documentation Standards
This structured approach enables organisations to systematically manage uncertainty while meeting regulatory obligations.
At T3 Consultants, we specialize in designing and enhancing custom risk management frameworks tailored to your sector, risk maturity, and regulatory landscape. Here’s how we can help:
- Risk Framework Design & Review: We align your RMF to ISO 31000, Basel, or PRA expectations.
- Regulatory Gap Analysis: Identify areas where your framework may fall short of UK and EU regulations.
- Board & Senior Stakeholder Workshops: Drive strategic buy-in and embed a risk-aware culture.
- Implementation Support: From policy drafting to training and monitoring dashboards.
- Tech & Data Integration: Helping you leverage RegTech and automation to manage risk more efficiently.
Whether you’re building your RMF from scratch or refreshing an outdated structure, our flipped consultancy model ensures expert delivery from day one.
Want to hire
Regulation Expert?
Book a call with our experts
