Basel 3.1: Navigating the New Frontiers of Global Banking Regulation

SHORTCOMINGS IN FINANCIAL RISK MITIGATION
The global financial crisis revealed significant shortcomings in the calculation of risk- weighted assets (RWAs) and capital ratios, defined as the ratio of capital held by firms to RWAs. The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) identified three elements as key to mitigating the severity of future financial crises:
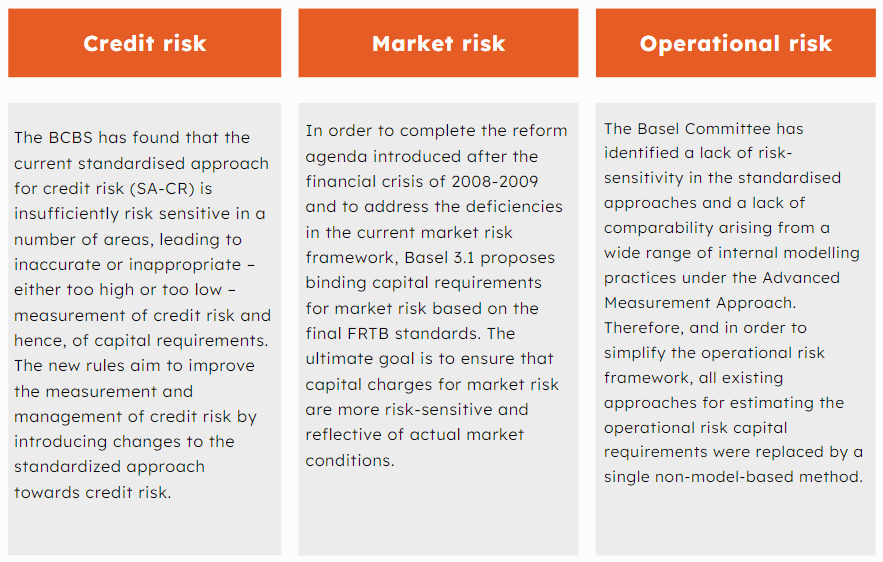
Per unite of risk, raise the quantity of capital in the financial system; increase the quality of capital held by financial institutions and improving the accuracy of risk measurement. Some of the key risks that Basel 3.1 seeks to address include credit, market and operational risk.
BASEL 3.1 - OVERVIEW
Basel 3.1 sets up updated rules designed to among others reinforce the risk-sensitivity of Risk-Weighted Asset (RWA) calculations. These standards come as a response to the observed variability in RWA calculations among different credit institutions. The most impactful measure to address that problem is the ‘output floor’, which sets a lower limit (‘floor’) on the capital requirements (‘output’) that banks calculate when using their internal models.
In some areas the EU deviates from Basel 3.1, thus reflecting EU specificities. For instance, the European Commission has included specific ESG-related rules. Banks will be required to demonstrate significant improvement in the sophistication and completeness of their approaches to ESG issues. Moreover, the proposed EU rules contain revisions to strengthen and make more consistent the fit and proper assessments for senior managers and members of banks’ management bodies. The CRR3 proposals will also bring significant changes to the Credit risk and Operational Risk framework.
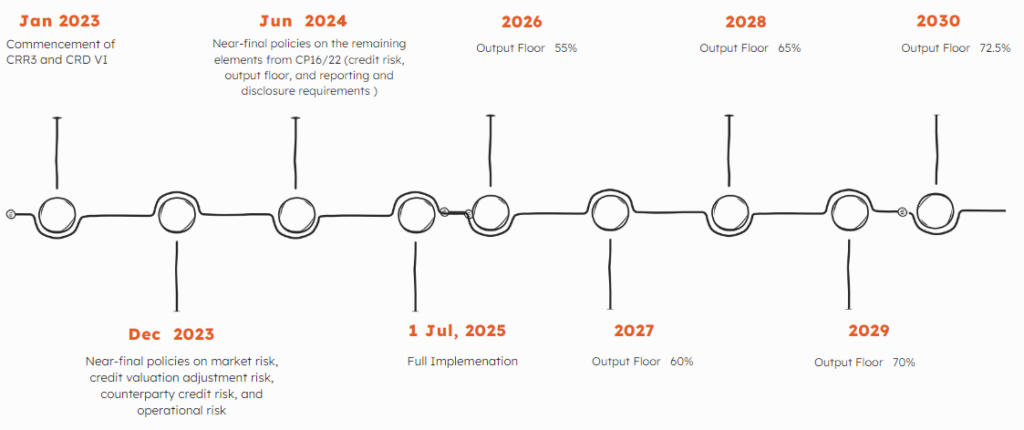
In the EU, initially scheduled for application in 2022, Basel 3.1 was postponed due to the impact of the global COVID-19 pandemic. However, as of June 27, 2023, trilogue negotiations among the EU Commission, Parliament, and Council led to a preliminary agreement, paving the way for the EU’s adoption of Basel 3.1 in the amended Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR3) and Capital Requirements Directive (CRD6). The forthcoming application of CRR3 and CRD6 is scheduled to commence on January 1, 2025, affording credit institutions a transition period for implementation.

AREAS OF COMPLEXITY
Basel 3.1 standards bring forth a range of complexities that financial institutions must understand comprehensively in order to navigate them effectively.
These are the most important areas of complexity:
Adapting to a Changing Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape within financial services changes regularly. Adapting to such changes is a considerable challenge. Financial institutions must stay ahead of regulatory shifts, interpreting how the new rules apply to their operations.
Comprehensive Risk Management Transformation
Basel 3.1 mandates a thorough transformation of credit institutions’ risk management practices and a reevaluation and recalibration of existing risk models, which are inherently complex. The overhaul extends to model risk governance, ongoing model enhancement processes, and ensuring model outputs remain reliable under diverse economic scenarios.
Data Quality
Basel 3.1 heavily relies on accurate and high-quality data for risk assessment. Ensuring the integrity and quality of data used in financial models poses a significant challenge since inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to erroneous model outputs, potentially causing financial losses and issues of non-compliance.
Blend of Expertise
Implementing Basel 3.1 requirements for model risk management demands a multidisciplinary approach. It requires collaboration between quantitative analysts, risk management experts, and regulatory specialists.
Advanced Technology Requirements
Building and maintaining the necessary technological infrastructure to support model risk management and validation processes is both complex and resource-intensive. Institutions need to invest in technology that can handle the demands of data-intensive risk models while ensuring security and scalability.
Establishing Robust Governance
Basel 3.1 places a premium on comprehensive governance frameworks that ensure accountability, transparency, and auditability of models. Creating and implementing these governance structures can be a multifaceted task, involving various stakeholders and complex processes.
Promoting Risk-Aware Culture
Basel 3.1 necessitates not only adherence to regulatory requirements but also the cultivation of a risk-aware culture within financial institutions. This cultural shift involves training personnel across the organization to understand model risks and the importance of validation, which can be an ongoing complexity.
Overview of how the Basel framework Basel 3 vs Basel 3.1 or 4

IMPORTANT DEADLINES
SERVICES
This publication has been prepared for general guidance on matters of interest only, and does not constitute professional advice. You should not act upon the information contained in this publication without obtaining specific professional advice. No representation or warranty (express or implied) is given as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in this publication, and, to the extent permitted by law, T3 Consultants Ltd, its members, employees and agents do not accept or assume any liability, responsibility or duty of care for any consequences of you or anyone else acting, or refraining to act, in reliance on the information contained in this publication or for any decision based on it.
